Yi Xu, PhD

Associate Professor
Contact
Center for Infectious and Inflammatory Diseases
2121 W. Holcombe Blvd.
Houston,
TX
77030
yi-xu1@tamu.edu
Phone: 713.677.7570
Fax: 713.677.7576
Xu Lab
Biography
Education and Training
- 1998, Ph.D. in biochemistry and molecular biology - University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston
- 1998 – 2004, Postdoc, Center for Infectious and Inflammatory Diseases, Institute of Biosciences and Technology, Texas A&M, Houston, TX
Research Interests
Bacteria and cancer; host-pathogen interactions; immune evasion.
Our lab is interested in the broad area of bacterial-host interactions. The manifestation and progression of infectious diseases are determined by the combined effects of bacterial factors and host reactions. Understanding these interactions is critical for combating infectious diseases. Furthermore, some of the bacterial – host interactions may cause alterations in host physiological or cellular processes that contribute to other types of diseases including cancer. 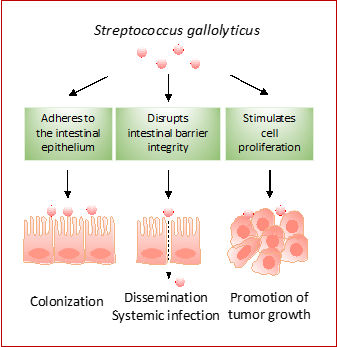
We are interested in Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus (Sgg), a gut pathobiont. Sgg, previously known as S. bovis biotype I, causes life-threatening infections such as bacteremia and infective endocarditis. It is also known to strongly correlate with CRC. Patients with Sgg infections have a 7-fold higher risk of developing colorectal adenoma/adenocarcinoma. Using a combination of in vitro cell cultures and mouse models, we demonstrated that Sgg actively promotes colon tumor growth. Sgg also possess the ability to disrupt the colonic epithelial barrier integrity and translocate across the epithelium. Thus, the gut occupies a central spot in the pathogenicity of Sgg. It provides a niche for Sgg to colonize the host and to spread to the circulation to cause infections. Residence of Sgg in the colon also influences gut homeostasis, thereby promoting the development of the colorectal cancer.
Our current research focus is to elucidate the specific Sgg factors that mediate gut colonization, dissemination, and promotion of tumor growth, and to delineate the host pathways targeted by these Sgg factors. In the long term, we hope to apply the knowledge to develop strategies to mitigate Sgg-induced pathologies.
Selected Publications
- Ritesh Kumar, John Taylor, Antrix Jain, Sung Yun Jung, and Yi Xu. “Modulation of the extracellular matrix by Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus and importance in cell proliferation”. PLoS Pathog. 2022 Oct;18(10):e1010894.
- Taylor, J. C., Gao, X., Xu, J., Holder, M., Petrosino, J., Kumar, R., Liu, W., Hook, M., Mackenzie, C., Hillhouse, A., Brashear, W., Nunez, M. P. & Xu, Y. ‘A type VII secretion system of Streptococcus gallolyticus gallolyticus contributes to gut colonization and the development of colon tumors’. (2021). PLoS Pathog 17, e1009182.
- Ritesh Kumar, Jennifer L. Herold, John Taylor, Juan Xu, and Yi Xu. ‘Variations among Streptococcus gallolyticus gallolyticus strains in connection with colorectal cancer’. Sci. Rep., 2018, 8(1):1514.
- Kumar, R., J. L. Herold, D. Schady, J. Davis, S. Kopetz, M. Martinez-Moczygemba, B. E. Murray, F. Han, Y. Li, E. Callaway, R. S. Chapkin, W. M. Dashwood, R. H. Dashwood, T. Berry, C. Mackenzie and Xu (2017). "Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus promotes colorectal tumor development." PLoS Pathog 13(7): e1006440.
- Wang, Y., S. A. Jenkins, C. Gu, A. Shree, M. Martinez-Moczygemba, J. Herold, M. Botto, R. A. Wetsel and Xu (2016). "Bacillus anthracis Spore Surface Protein BclA Mediates Complement Factor H Binding to Spores and Promotes Spore Persistence." PLoS Pathog 12(6): e1005678.
- Jenkins SA and Xu Y. ‘Characterization of Bacillus anthracis persistence in vivo’. PLoS One, 2013 Jun 4;8(6):e66177.
- Gu, C., Jenkins, S. A., Xue, Q., and Xu, Y. ‘Activation of the Classical Complement Pathway by Bacillus anthracis Is the Primary Mechanism for Spore Phagocytosis and Involves the Spore Surface Protein BclA’. J Immunol, 2012, 188(9):4421-31.
- Qiong Xue, Chunfang Gu, Jose Rivera, Magnus Hook, Xiwu Chen, Ambra Pozzi, and Yi Xu. ‘Entry of Bacillus anthracis spores into epithelial cells is mediated by the spore surface protein BclA, integrin α2β1, and complement component C1q’. Cell Microbiol, 2011, 13(4): 620-34.
- Qiong Xue, Sarah A. Jenkins, Chunfang Gu, Emanuel Smeds, Qing Liu, Ranga Vasan, Brooke Russell, and Yi Xu. ‘Bacillus anthracis spore entry into epithelial cells is an actin-dependent process requiring c-Src and PI3K’. PloS One. 2010, Jul 20; 5(7): e11665.
- Scott E. Evans, Yi Xu, Michael J. Tuvim, and Burton F. Dickey. ‘Inducible Innate Resistance of Lung Epithelium to Infection’. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010, 72:413-435.
- Brown EL, Xue Q, Jiang ZD, Xu Y, Dupont HL. ‘Pretreatment of epithelial cells with rifaximin alters bacterial attachment and internalization profiles.’ Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 Jan;54(1):388-96.
- Evans SE, Scott BL, Clement CG, Larson DT, Kontoyiannis D, Lewis RE, Lasala PR, Pawlik J, Peterson JW, Chopra AK, Klimpel G, Bowden G, Hook M, Xu Y, Tuvim MJ, Dickey BF. ‘Stimulated innate resistance of lung epithelium protects mice broadly against bacteria and fungi’. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2010, 42: 40-50, PMID: 19329554.
- Brooke H. Russell, Qing Liu, Sarah A. Jenkins, Michael J. Tuvim, Burton F. Dickey, and Yi Xu. ‘In vivo demonstration and quantification of intracellular Bacillus anthracis in lung epithelial cells’. Infect. Immun., 2008, 76(9): 3975-3983.
- Brooke H. Russell, Ranga Vasan, Douglas R. Keene, Theresa M. Koehler, and Yi Xu. ‘Potential dissemination of Bacillus anthracis utilizing human lung epithelial cells’. Cellular Microbiology. 2008, 10: 946-967.
- Brooke H. Russell, Ranga Vasan, Douglas R. Keene, and Yi Xu. ‘Bacillus anthracis internalization by human fibroblasts and epithelial cells’. Cellular Microbiology. 2007, 9(5): 1262-1274
- Liu, Q., K. Ponnuraj, Y. Xu, V. K. Ganesh, J. Sillanpaa, B. E. Murray, S. V. Narayana and M. Hook (2007). "The Enterococcus faecalis MSCRAMM ACE Binds Its Ligand by the Collagen Hug Model." J Biol Chem 282(27): 19629-19637.
- Runlin Han, Antoni Zwiefka, Clayton C. Caswell, Yi Xu, Douglas R. Keene, Ewa Lukomska, Zhihong Zhao, Magus Hook, and Slawomir Lukomski. ‘Assessment of prokaryotic collagen-like sequences derived from streptococcal Scl1 and Scl2 proteins as a source of recombinant GXY polymers’. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2006 March, 72(1):109-15.
- Yinong Zong, Yi Xu, Xiaowen Liang, Douglas R. Keene, Agneta Höök, S. Gurusiddappa, Magnus Höök, and Sthanam VL Narayana. ‘A “collagen hug” model for Staphylococcus aureus CNA binding to collagen’. EMBO J. 2005 Dec 21;24(24):4224-36.
- Kim JK, Xu Y, Keene DR, Gurusiddappa S, Liang X, Wary KK, Höök M. ‘A novel binding site in collagen type III for the integrins, alpha 1beta 1 and alpha 2beta 1’ J Biol Chem. 2005, 280(37):32512-20
- Bowden MG, Chen W, Singvall J, Xu Y, Peacock SJ, Valtulina V, Speziale P, Höök M. ‘Identification and preliminary characterization of cell-wall-anchored proteins of Staphylococcus epidermidis’ Microbiology. 2005 May;151(Pt 5):1453-64.
- Humtsoe JO, Kim JK, Xu Y, Keene DR, Höök M, Lukomski S, Wary KK. ‘A streptococcal collagen-like protein interacts with the alpha 2beta 1 integrin and induces intracellular signaling’. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280(14):13848-57.
- Yi Xu, Xiaowen Liang, Yahua Chen, Theresa M. Koehler, and Magnus Höök. ‘Identification and biochemical characterization of two novel collagen binding MSCRAMMs of Bacillus anthracis’. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 179 (50):51760-8.
- Jouko Sillanpää, Yi Xu, Sreedhar R. Nallapareddy, Barbara E. Murray and Magnus Höök. ‘A family of putative MSCRAMMs from Enterococcus faecalis’. Microbiology, 2004, 150(Pt 7):2069-78.
- Karthe Ponnuraj, M. Gabriela Bowden, Stacey Davis, S. Gurusiddappa, Dwight Moore, Damon Choe, Yi Xu, Magnus Höök, and Sthanam V. L. Narayana. 2003. ‘A “dock, lock, and latch” structural model for a Staphylococcal adhesin binding to fibrinogen’. Cell 115(2): 217-28.
- Yi Xu, Jorge M. Rivas, Eric L. Brown, Xiaowen Liang, and Magnus Höök. 2004. ‘The virulence potential of the staphylococcal adhesin CNA in experimental arthritis is determined by its affinity for collagen’, J. Infect. Dis., 189:2323-2333.
- Pikas, D. S., Brown, E. L, Gurusiddappa, S., Lee, L. Y., Xu, Y., Höök, M., 2003. ‘Decorin-binding sites in the adhesin DbpA from Borrelia burgdorferi: a synthetic peptide approach’, J. Biol. Chem., 278: 30920-6
- Ponnuraj, K., Xu, Y., Moore, D., Deivanayagam, C. C., Boque, L., Höök, M., Narayana, S. V., 2002, ‘Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of Ace: a collagen-binding MSCRAMM from Enterococcus faecalis’, Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1596: 173-6
- Yi Xu, Douglas R. Keene, Janusz M. Bujnicki, Magnus Höök, and Slawomir Lukomski. 2002. ‘Streptococcal Scl1 and Scl2 proteins form collagen-like triple helices’. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 27312-27318.
- Livia Visai, Yi Xu, Fabrizia Casolini, Simonetta Rindi, Magnus Höök and Pietro Speziale. 2000. ‘Monoclonal antibodies to CNA, a collagen-binding microbial surface component recognizing adhesive matrix molecules, detach Staphylococcys aureus from a collagen substrate’. J. Biol. Chem. 275: 39837-39845.
