Margie Moczygemba, PhD

Associate Professor
Director, HT Flow Cytometry Analysis & Cell Sorting Core Facility
Advisor to the Dean for Internal Affairs – School of Engineering Medicine
Contact
TMC3-Texas A&M Health
7255 Helix Park Ave. Room 2009
Houston,
TX
77030
mmoczygemba@tamu.edu
Phone: 713.677.8114
Hight Throughput Flow Cytometry Analysis and Cell Sorting
Biography
- IBT Associate Director for Academic Affairs
Education and Training
- B.S. Biology, Texas A&M University, Kingsville, TX, 1989
- M.S. Biology, Texas A&M University, Kingsville, Texas, 1992
- Ph.D., Molecular Immunology and Pathology, State University of New York at Stony Brook, Stony Brook, N.Y., 1997
- Postdoctoral Fellowship, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, 1997-2002
Research Interests
The research focus of the Moczygemba laboratory is to develop interventional strategies that block allergic inflammation through our increased understanding of cytokine signaling and eosinophil biology. The eosinophil and its major activator, IL-5, play an important role in the pathogenesis of allergies and asthma. Thus, one of our goals is to understand regulatory mechanisms that control the intensity and duration of IL-5-mediated eosinophilic signaling. To this end, we employ various cellular, immunological, and biochemical techniques to help us identify novel targets capable of modulating inflammatory signals triggered by eosinophils.
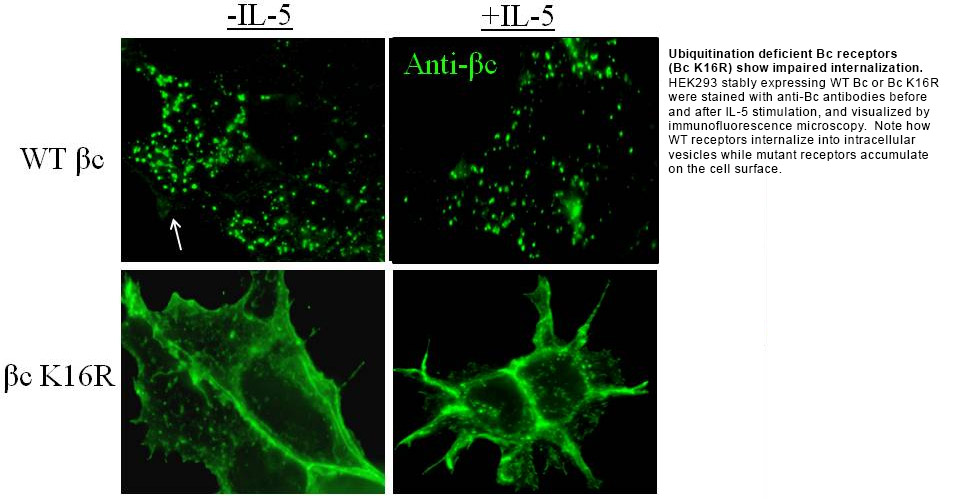
One area of deep interest in our lab is the molecular characterization of IL-5 receptor ubiquitination especially that associated with the common beta chain (betaC). Previously we demonstrated that the betaC cytoplasmic tail was ubiquitinated and degraded by proteasomes after IL-5 stimulation. We have since identified a cluster of three membrane-proximal lysine residues (K457, K461, and K467) on betaC that are required for JAK1 and JAK2 binding, and betaC ubiquitination. Importantly, we found that in the absence of these three lysine residues, bc ubiquitination, endocytosis and signaling were significantly impaired, indicating that JAK binding to bc is an essential step in IL-5 receptor regulation.
In a related project associated with allergic inflammation, we are collaborating with our colleagues from MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston. The major focus of this project is to harness the activation of lung innate immunity using aerosolized TLR Ligands to modulate the asthmatic immune response. Recent findings indicate that administration of aerosolized antigen with a specific combination of TLR ligands has a major effect on the immunomodulation of the allergic IgE response and eosinophilic inflammation in a murine model of experimental asthma. Insight into these immunomodulatory mechanisms could potentially identify novel targets for controlling inflammation associated with asthma.
Selected Publications
- Amini-Vaughan, Z., Martinez-Moczygemba, M., Huston, DP. Therapeutic strategies for harnessing human eosinophils in allergic inflammation, hypereosinophilic disorders, and cancer. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep, 12(5):402-412, 2012 PMID:22875242
- Lei JT, Mazumdar, TM, M Martinez-Moczygemba: Three lysine residues in the common beta chain of the IL-5 receptor are required for Janus kinase-dependent receptor ubiquitination, endocytosis and signaling. J Biol Chem. 2011 Sep 30. (Epub ahead of print).
- Lee, M-S., Cherla, R.P., Jenson, M.H., Leyve-Illades, D., Martinez-Moczygemba, M., and Tesh, V.L: Shiga toxins induce autophagy leading to differential signaling pathways in the toxin-sensitive and toxin-resistant human cells. Cell Microbiol 13(10):1479-1496, 2011. PMID:21722286.
- Martinez-Moczygemba, M, Doan, ML, Elidemir, O, Fan, LL, Cheung, SW, Lei, JT, Moore, JP, Tavana, G, Lewis, LR, Zhu, Y, Muzny, DM, Gibbs, RA, Huston, DP. 2008. "Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis Due to Deletion of the GM-CSFR? Gene in the X-Chromosome Pseudoautosomal Region 1." J Exp Med, 205(12):2711-6. Epub Oct 27, 2008
- Lei, JT, Martinez-Moczygemba M. 2008. "Separate endocytic pathways regulate IL-5 Receptor Internalization and signaling." J Leukoc Biol 84:499-509.
- Martinez-Moczygemba M, DP Huston, Lei JT. 2007. "JAK kinases control IL-5 receptor ubiquitination, degradation and internalization." J Leukoc Biol 81(4):1137-48.
- Martinez-Moczygemba M, DP Huston. 2003. "Biology of common ? receptor-signaling cytokines: IL-3, IL-5, and GM-CSF." J Allergy Clin Immunol 112(4):653-665.
- Huang JC, M Martinez-Moczygemba, AP Nguyen, DP Huston. 2003. "Modulating the interleukin-5 response in Asthma. In: Therapeutic Targets of Airway Inflammation." Eds. NT Eissa and DP Huston; Marcel-Dekker, Inc., New York, New York. 177:495-518.
- Foster PS, M Martinez-Moczygemba, DP Huston, DB Corry. 2002. "Interleukins 4, 5, and 13: emerging therapeutic targets in allergic disease." Pharmacol Ther 94:253-264.
- Martinez-Moczygemba M, DP Huston. 2001. "Proteasome regulation of ?c signaling reveals a novel mechanism for cytokine receptor heterotypic desensitization." J Clin Invest 108:1797-1806.
- Huston DP, MM Huston, RR Dickason, M Martinez-Moczygemba. 2000. "Interleukin-5, a therapeutic target in allergic inflammation." Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc 111:46-60.
- Martinez-Moczygemba M, MJ Gutch, DL French, NC Reich. 1997. "Distinct STAT structure promotesinteraction of STAT2 with the p48 subunit of the interferon-a stimulated transcription factor, ISGF3." J Biol Chem 272:20070-20076.
- Kotanides H, M Martinez-Moczygemba, MF White, NC Reich. 1995. "Characterization of interleukin-4 nuclear activated factor/STAT and its activation independent of the insulin receptor substrate proteins." J Biol Chem270:19481-19486.
